AUTHOR: Ing. Matteo Lucarelli
TUTORS: Ing. Giovanni Franchi
INTERNSHIP: C.M.B. Milano
MASTER: Master in Project management in Construction works with BIM
La Tesi rappresenta il connubio tra le nozioni apprese durante le lezioni del Master e l’esperienza lavorativa svolta all’interno del cantiere SPARK ONE a Milano Rogoredo con il General Contractor CMB. L’edificio simbolo della riqualificazione dell’area presenta molteplici aspetti che distinguono sia il progetto sia la sua gestione e che hanno permesso la concretizzazione dell’Integrated Project Delivery (IPD), ossia il cambio di paradigma dal processo step by step contrassegnato dall’individuo ad un Collaborative Work and Scope (CWS) tra tutti gli attori coinvolti.
Il Core della Tesi si basa sull’applicazione del BIM Project Management in tutti le sue fasi: Initiating, Plannig, Execution, Monitoring e Closing, focalizzandosi sugli aspetti del coordinamento multidisciplinare, sul 5D (I.T.O.) e sul CDE Management. Dallo studio delle analisi S.W.O.T. e P.E.S.T.E.L. si evince che l’applicazione del BIM nel Project management sia fondamentale per la digitalizzazione delle costruzioni. CMB ormai da anni ha implementato nella gestione dei progetti la metodologia del building information management potendo ottimizzare a livello di gestione, tempi e costi l’intera gestione della commessa e migliorando/aggiornando costantemente lo scambio informativo tra gli stakeholder mediante il CDE.
La progettazione costruttiva sviluppata in ambiente BIM ha delineato la dimensione del phygital, ossia la perfetta corrispondenza tra modello ed elementi materiali, in virtù di un processo del Design to Build; aspetto cardine di tale processo è il rispetto del LOA Level of Assurance senza il quale si avrebbero gravi conseguenze in ogni step della commessa. Rispetto alle precedenti fasi di progettazione, nello step del progetto costruttivo emergono tutte le problematiche legate agli aspetti normativi, all’approvvigionamento dei materiali (in particolare la difficoltà durante il periodo del COVID-19) agli aspetti economici-finanziari, alle lavorazioni e alle scelte talvolta obbligate per non incorrere in criticità. Gli step di Code – Model Checking hanno permesso la possibilità di verificare le quantità in fase d’offerta, la qualità dei metadata in entrata e in uscita e di limitare errori di progettazione e quindi di non avere rallentamenti in cantiere.
Il CDE utilizzato nel cantiere è stato customizzato per le esigenze della commessa garantendo non solo i classici ambienti di scambio (WIP – Share – Publish – Archive), validazione e download elaborati ma anche un metodo per l’estrazione dei dati finalizzati al controllo dell’avanzamento della progettazione. Inoltre, è stato implementato e gestito uno spazio dedicato agli attori “estranei” alla progettazione ove inserire report, registri consultabili da chiunque senza il rischio di modificare il flusso approvativo del progetto.
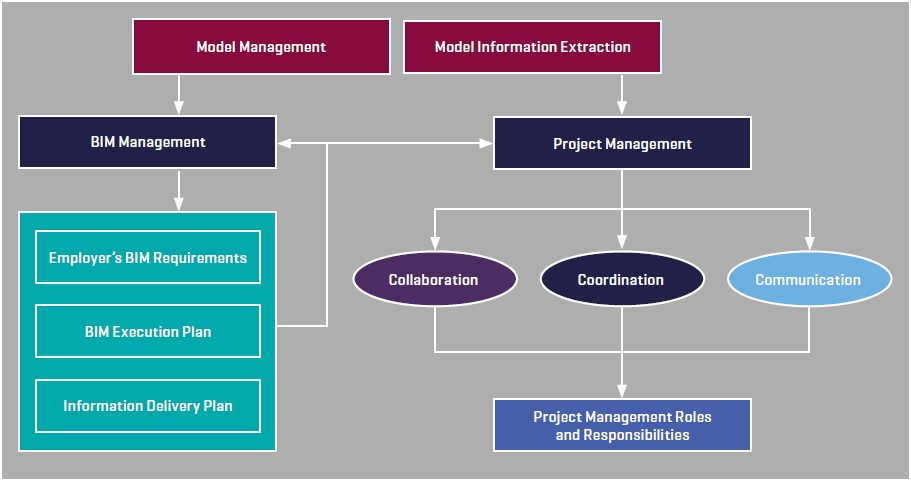
In conclusione, il percorso di studio altamente multidisciplinare e pioneristico offre un duplice vantaggio: Il primo, come emerge dallo schema sopra, evidenza l’importanza del BIM Project Manager poiché grazie alla metodologia del IPD – quindi l’utilizzo del BIM e del CDE – potrà migliorare il modo di comunicare, collaborare, coordinare e quindi di poter prendere la migliore decisione nel minor tempo possibile. Ciò permetterà il raggiungimento del SOW, garantendo tempi costi e qualità del progetto; il secondo, offre la possibilità di essere competitivi in un mercato in continuo aggiornamento e cambiamento formando la figura del project manager dell’Industria 4.0.
BIM: BETTER INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
FOR INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS:
The Thesis describes the combination of the concepts learned during the Lessons of the Master and the work experience carried out within the SPARK ONE bulding site in Milan Rogoredo with the General Contractor CMB. The building symbol of the redevelopment of the area has many aspects that distinguish both the project and its management, and it has allowed the realization of integrated project delivery (IPD) so the paradigm shift from the step by step process marked by the individual to a Collaborative Work and Scope (CWS) between all the actors involved.
The Core of the Thesis is based on the application of BIM Project Management in all its phases: Initiating, Plannig, Execution, Monitoring and Closing, focusing on the aspects of multidisciplinary coordination, on 5D (I.T.O.) and on CDE Management. As can be seen from the S.W.O.T. and P.E.S.T.E.L. analyses. it emerges that the application of BIM to Project management is fondamental for the digitization of buildings. For years now, CMB has implemented the BIM methodology in project and construction management, being able to optimize the entire workflow in terms of management, time and costs and constantly improving/updating the information exchange between stakeholders through the CDE.
The construction design developed in the BIM environment has outlined the dimension of the phygital, that is the perfect correspondence between model and material elements, in order to reach a Design to Build process; The key aspect of this process is compliance with the LOA Level of Assurance without which there would be serious consequences in every step of the order. Compared to the previous design phases, in the step of the construction project all the problems related to the law aspects, the procurement of materials (in particular the difficulty during the COVID-19 period) to the economic-financial aspects, to the processes and to the choices sometimes forced to avoid incurring critical issues emerge. The Code – Model Checking steps have allowed the possibility to verify the quantities in the bidding phase, the quality of the incoming and outgoing metadata and to limit design errors, as not to have slowdowns on site.
The CDE used in the construction site has been customized for the needs of the order, guaranteeing not only the classic exchange environments (WIP – Share – Publish – Archive), validation and processed downloads but also a method for extracting data aimed at controlling the development of the design. In addition, a space dedicated to “extraneous” actors to the design has been implemented and managed where to insert reports, registers that can be consulted by anyone without the risk of modifying the approval flow of the project.
In conclusion, the highly multidisciplinary and pioneering course of study offers a double advantage. The first, as emerges from the following diagram, highlights the importance of BIM Project Manager because thanks to the IPD methodology – therefore the use of BIM and CDE – it will be able to improve the way of communicating, collaborating, coordinating and therefore being able to make the best decision in the shortest possible time. This will allow the achievement of the SOW, guaranteeing time costs and quality; the second offers the opportunity to be competitive in a constantly updated and changing market by forming the figure of the Industry 4.0 project manager.