AUTHOR: Francesca Tomasoni
TUTORS: Prof. Crespi – Andrea Sgambati
SOCIETA’: Mediobanca innovation services
MASTER: Master in “Gestione energetica di edifici e infrastrutture” II liv. a.a 2019/2020
Il lavoro di tesi si inserisce nel processo di progettazione di un nuovo quartiere residenziale a Lentate sul Seveso.
Lo scopo di questa tesi, che si concentra su uno degli edifici residenziali del quartiere, è quello di calcolare le prestazioni energetiche dell’edificio individuato come caso studio (edificio di progetto base) al fine di individuare azioni migliorative per renderlo un edificio n-ZEB (edificio ottimizzato) mediante il software di modellazione TERMOLOG.
Il lavoro è strutturato in due parti. La prima si concentra sugli aspetti normativi e teorici legati alla progettazione di edifici ad elevate prestazioni energetiche, nella seconda, a partire dall’ottimizzazione di un caso studio, viene simulato il progetto di un edificio n-ZEB.
Nella prima parte, in particolare nel primo capitolo, si approfondisce il tema più generale della prestazione energetica degli edifici, modalità di calcolo e il relativo quadro normativo e tecnico. Sono analizzati i parametri relativi al fabbricato, agli impianti, gli indici di prestazione energetica calcolati secondo il metodo dell’edificio di riferimento, nonché i requisiti minimi richiesti per legge per la progettazione di un “Near Zero Energy Building”. Nel secondo capitolo sono approfonditi l’ampio tema degli edifici n-ZEB, i requisiti e le caratteristiche da introdurre in un progetto affinché vengano soddisfatte le verifiche di legge e ottimizzate al meglio le prestazioni energetiche dell’edificio, sia in termini di involucro e sistemi passivi, sia di componenti impiantistiche e di ventilazione. Nel terzo capitolo viene introdotto il tema della modellazione energetica e descritto il modulo progettista del software TERMOLOG, programma scelto per la modellazione del caso studio, il calcolo dei risultati e le verifiche n-ZEB.
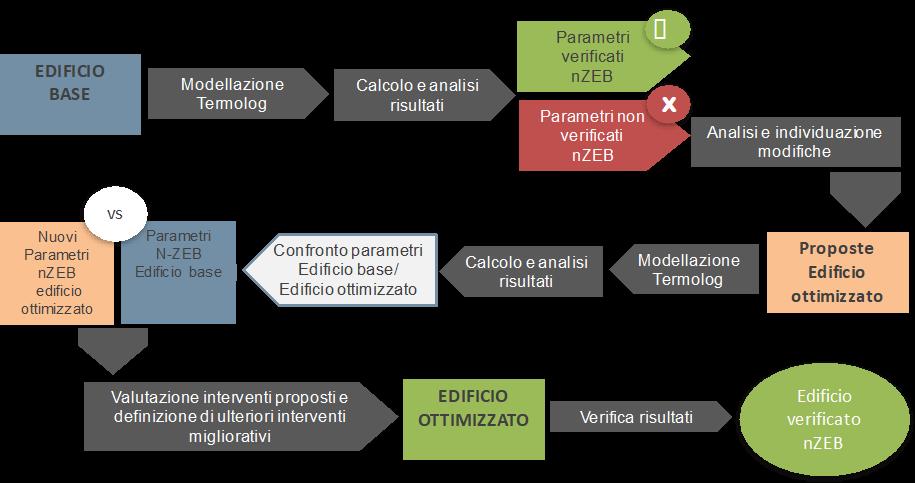
FASI DEL PROCESSO: modellazione dell’edificio base – calcolo e analisi dei risultati- ottimizzazione – definizione dell’edificio nZEB ottimizzato
Nella seconda parte, in particolare nel quarto capitolo, è descritto e inquadrato il caso studio, con riferimento al concept e al masterplan di progetto, a seguire sono specificate le caratteristiche morfologiche e la destinazione d’uso dell’edificio residenziale con negozi al piede oggetto della tesi. A seguire è analizzato l’intero processo utilizzato per definire il progetto dell’edificio ottimizzato, riportato sinteticamente in Figura II.
Nel quinto capitolo è descritta la costruzione del modello dell’edificio di progetto (edificio base) in TERMOLOG, vengono calcolati e analizzati i primi risultati e individuati i miglioramenti sino alla definizione dell’edificio n-ZEB ottimizzato. Nello specifico, definito il modello dell’edificio base e calcolati i risultati, si analizzano sia parametri relativi all’involucro, come il coefficiente globale di scambio termico (H’T)e l’area solare equivalente estiva (Asol, est), sia gli indici legati agli impianti, come gli indici di prestazione termica utile per riscaldamento e raffrescamento (EPHnd, EPCnd), l’indice di prestazione globale (EPgl,tot)e la copertura % dei consumi da fonti rinnovabili. A seguire sono individuati gli interventi migliorativi e le modifiche necessarie al soddisfacimento dei requisiti n-ZEB rispetto all’edificio di riferimento. Tra questi troviamo modifiche dell’involucro, in particolare dei serramenti e relative trasmittanze, e la ri-distribuzione delle aperture e delle vetrine a piano terra. Relativamente agli impianti, si individua l’introduzione di sistemi impiantistici per la produzione di energia elettrica da fonti rinnovabili (fotovoltaico e solare termico) e l’introduzione di un sistema di VMC per il miglioramento del comfort indoor.
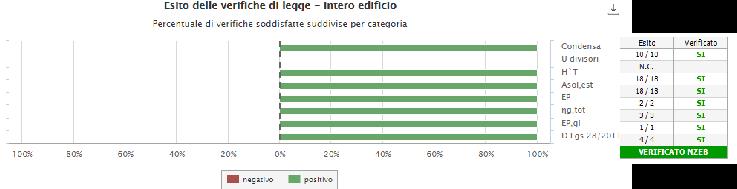
In conclusione, viene calcolato e definito il modello dell’edificio ottimizzato verificato come edificio ad energia quasi zero (Figura III), dalle prestazioni migliorate rispetto all’edificio inizialmente progettato, sia in termini energetici che di comfort.
FOR INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS
The thesis work is part of the design process of a new residential area in Lentate sul Seveso.
The purpose of this thesis which focuses on one of the residential buildings in the neighborhood, is to calculate the energy performance of the building selected as a case study (basic project building) in order to identify improvement actions to make it an n-ZEB building (optimized building) using TERMOLOG modeling software.
The work is structured in two parts. The first one focuses on the regulatory and theoretical aspects related to the design of buildings with high energy performance. In the second part, the design of an n-ZEB building is simulated starting from the optimization of a case study.
In the first part, in particular in the first chapter, the general theme of the energy performance of buildings, calculation methods and the related regulatory and technical framework is analyzed. The parameters relating to building, systems, energy performance indices are calculated according to the reference building method, and the minimum legal requirements to design a “Near Zero Energy Building” are analyzed. The second chapter examines the broad theme of n-ZEB buildings, requirements and characteristics in terms of envelope and passive-systems, plant components and ventilation. The third chapter introduces the topic of energy modeling and describes the designer module of TERMOLOG software, the program chosen for modeling the case study, the calculation of the results and the n-ZEB verifications.
In the second part, in particular in the fourth chapter, the case study is described and framed with reference to the concept and the project masterplan, morphological characteristics and use: apartments and shops at the ground floor. The entire process used to define the optimized building design is analyzed below, summarized in Figure II.
The fifth chapter describes the construction of the project building model (base building) in TERMOLOG. The first results are calculated and analyzed and improvements are identified up to the definition of the optimized n-ZEB building. Specifically, once the basic building model has been defined and the results calculated, both parameters relating to the envelope and systems are analyzed: global heat exchange coefficient (H’T) and the equivalent summer solar area (Asol, east), thermal heating and cooling performance index (EPHnd, EPCnd), global performance index (EPgl, tot) and the percentage of consumption covered from renewable sources. The improvements and changes necessary to meet the n-ZEB requirements with respect to the reference building are identified below. These include changes to the envelope (windows and related transmittances), and the re-distribution of the openings and shop windows on the ground floor. With regard to the systems, the introduction of plant systems to produce electricity from renewable sources (photovoltaic and solar panels) and the introduction of a VMC system to improve indoor comfort are identified.
In conclusion, the optimized building model verified as a nearly zero energy building is calculated and defined (Figure III) with improved performance compared to the building initially designed, both in terms of energy and comfort.