Author: Eng. Jolin Babu Cherukara
Tutor: Eng. Giovanni Franchi
Master: BIM Management in Construction Works
The utilization of Building Information Modeling (BIM) & Digital technology was crucial in successfully constructing and engineering the “Community Hub” project. The implementation of BIM went beyond just a tool; it was an essential factor in the project’s success due to its complexity and unique requirements. The project demanded a sophisticated BIM approach to accommodate intricate architectural designs, complex engineering specifications, and strict construction standards. The ”
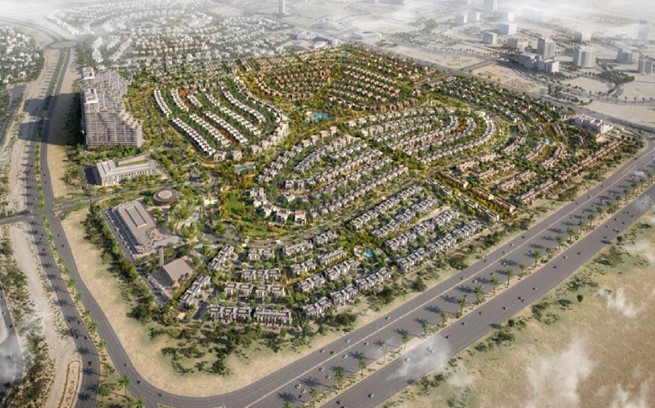
The ‘Community Hub’ is a unique wellness-oriented community development project in Dubai. It is strategically located near thriving communities and developments, aiming to establish a distinctive lifestyle for residents. The project emphasizes wellness, health, well-being, and sustainability, creating a walkable community that promotes a healthy lifestyle and offers activities for individuals of all ages within a sustainable environment. BIM technology has been pivotal in this upscale residential community, facilitating the seamless integration of intricate design and diverse functionalities, ultimately attaining LEED Cities & Communities and Fitwell Community Certification. The project has set new standards in efficiency, sustainability, and innovation, highlighting BIM’s potential to reshape the future of construction.
BIM technology has revolutionized the architectural, engineering, and construction industry by providing a data-driven digital platform for creating, managing, and analyzing building and infrastructure projects. Its role in the ‘Community Hub’ project in Dubai is a testament to its value. BIM enhances quality, collaboration, and decision-making, while reducing errors, ultimately leading to more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable projects throughout their entire lifecycle. The ‘Community Hub’ project, with its intricate architectural designs and complex engineering specifications, is a prime example of how BIM can reshape the future of construction, setting new standards in efficiency, sustainability, and innovation.
The thesis focuses on exploring the critical role of a high-quality Building Information Model (BIM) during the design stage of a project, from the initiation to the design review and coordination until the closing of the design stage. This plays a crucial role in ensuring that the client’s requirements are met and exceeded. A high-quality BIM-based model significantly enhances communication, coordination, and collaboration and allows for accurate simulation and analysis of the building’s performance, aligning the final product with the client’s expectations.
In this project and thesis, we have explained the implementation of the Master plan project and its challenges. We have utilized Automated BIM Health check, standard check using BIM interoperability toll, design review, and clash coordination process. Automated Quality Assurance & Quality Control (AQAQC) of Building Information Models (BIM) can be employed to ensure that the models conform to client-standard project protocols and guidelines. This can be implemented using software that checks the BIM model for compliance with the Building Execution Plan (BEP), which outlines the BIM protocols for a specific project. This process checks for missing or incorrect data, incorrect geometry, and conflicts between disciplines. It provides a report highlighting any problems found in the correction model. This ensures that the BIM model meets the required standard and that the building will be constructed as per the design intent.
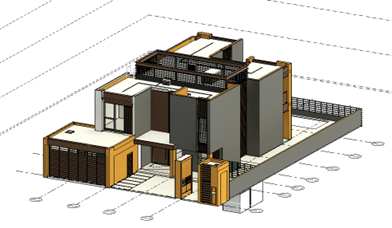
CGI (Computer Generated Imagery) of the Enlarged area from the Community Hub Project in Dubai.
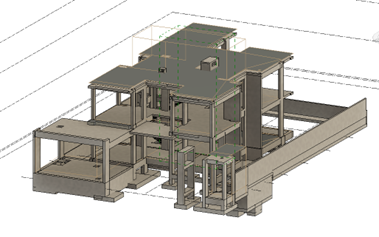
A BIM-based 3-dimensional model of Architectural & structural components
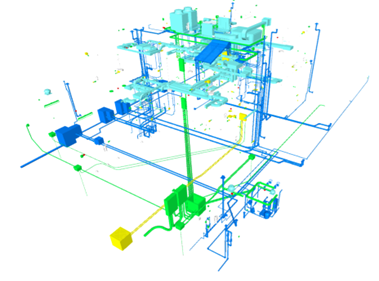
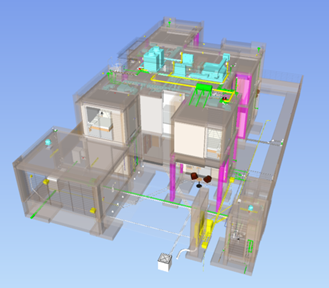
A BIM-based 3-dimensional model of MEPF and the Combined Federated Model components
While interning and working at Ellisdon in the United Arab Emirates, I held the esteemed position of BIM Manager for Middle East projects. I mainly focused on projects for our clients in Dubai and the Northern Emirates. As the Client Representative BIM Manager, my primary responsibility was supporting the client in the BIM review and ensuring all the design consultant BIM models aligned with the prescribed Employer Information requirement (EIR) and the client BIM Protocols and Standards.
My role involved conducting weekly meetings and reviewing approximately 10–15 projects on behalf of the client to ensure quality assurance and control (QA/QC) compliance. I have implemented a process that involved cross-referencing data with the project’s BIM Protocols (MIDP/TIDP), the standard Project QA/QC checklist, and relevant appendices using Microsoft Excel. This automation significantly expedited the QA/QC process, improving efficiency and accuracy for project guidelines.
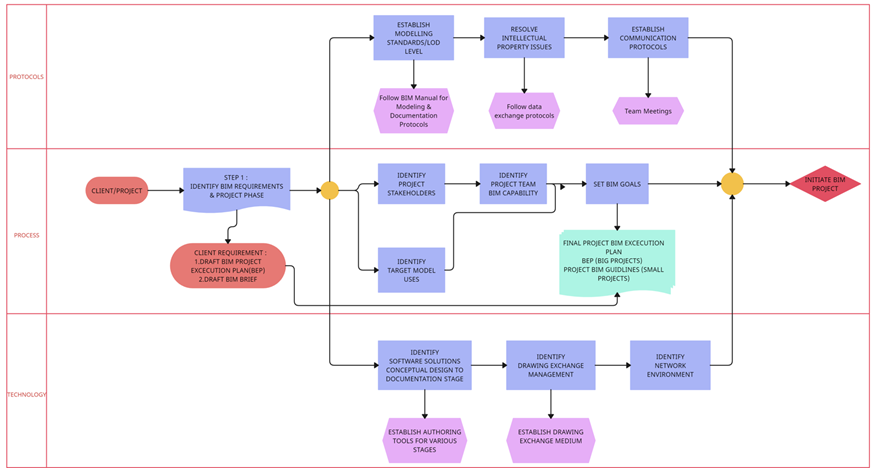
PROJECT INITIATION
Several pivotal steps must be considered when commencing a BIM project. Initially, it is crucial to delineate the project’s Protocol, scope, and standards, as these elements form the groundwork for the entire project. Subsequently, the process involves identifying the workflow, collaboration methods, and coordination procedures. Finally, selecting the most suitable digital technology necessitates the choice of appropriate BIM software, tools, and platforms that are in alignment with the project’s requirements and objectives.
Flowchart for the BIM Project initiation process
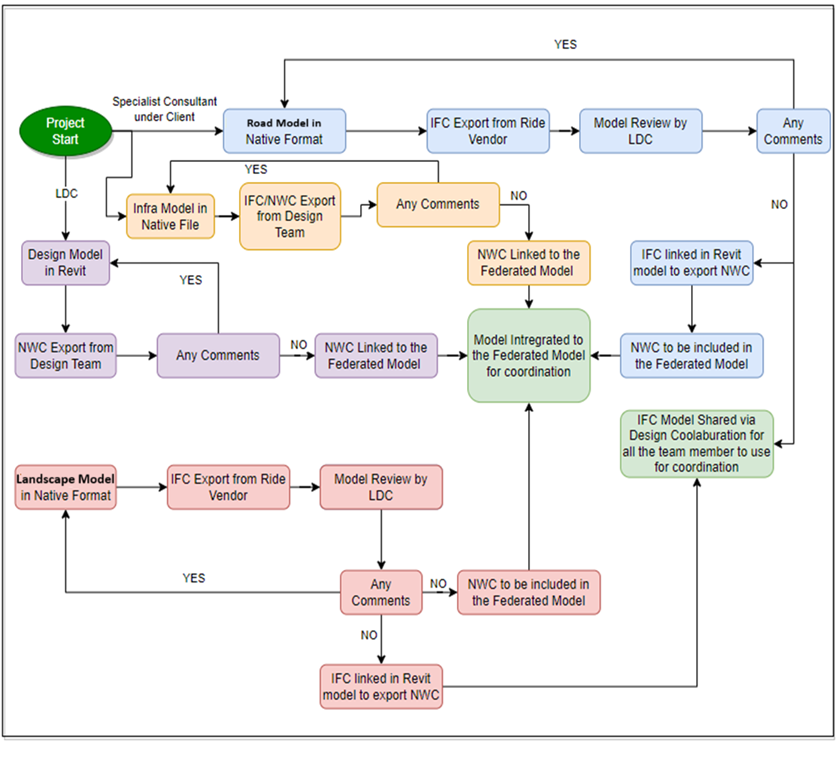
Coordination Between Different Consultants
The project requirements delineate the specialized consultants’ responsibility in developing the model across various BIM environments, such as Autodesk Revit and Civil 3D, etc. Effective coordination and communication between the specialist and lead design consultants are essential to this process. The proposed workflow is specifically crafted to foster collaboration between consultants and the client, focusing on this master plan project involving diverse design consultants and specialists.
After implementing the workflow, we conducted case studies to examine the frequency and distribution of issue types across various disciplines and analyze their resolution rates. Each case study involved an independent investigation of the issues, utilizing practitioner documentation and insights from relevant meetings.
The analysis was iterative and involved revisiting issue categories, terminology, and examples multiple times to ensure a comprehensive understanding and resolution.
Clash detection, Coordination analysis & Resolution Workflow
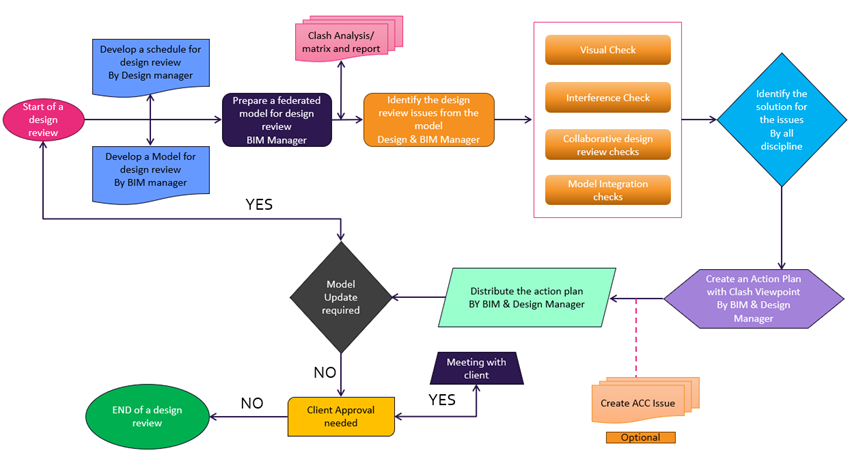
DESIGN REVIEW
The BIM design review process is a methodical approach to comprehensively evaluate and validate different aspects of a building’s design. It involves several key steps, including establishing the process framework and identifying roles and stakeholders. The subsequent steps include forming specialized review teams, utilizing BIM tools for feedback and annotation, presenting the model for initial feedback, engaging in discussions and seeking clarifications, revising the design iteratively, and finally documenting the process and obtaining final approval.
Design Review Process Workflow
Before implementing this process, the Design review, clashes coordination and analysis, the Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC) process for LDC BIM models used to require a substantial two-man week’s effort, equivalent to 80 to 90 hours of work each week.
Unresolved issues had to be addressed during detailed model coordination, resulting in increased costs and schedule delays. Considering the typical duration of a project of this magnitude, around nine months or 36 weeks, the impact of this transformation is significant.
Through the implementation of the new process, the QA/QC time was reduced from an initial 648 hours (equivalent to 72 man-days) to a streamlined 108 hours (or 12 man-days). This advancement resulted in a staggering 83.3% increase in efficiency, resulting in substantial time savings and improved precision and productivity.
CONCLUSION
The study delves into the challenges of current BIM-based building design coordination processes, including unnoticed coordination issues, ineffective problem resolution, and poorly documented coordination problems. It revealed that 40% of design issues remained unresolved at the end of the design coordination stage.
The research focused on scrutinizing the BIM design coordination process, encompassing design issue identification, resolution, and documentation. It was discovered that nearly two-thirds of the analyzed issues were design-based and originated from modelling errors, often triggered by physical design issues. Furthermore, design issues were less likely to be addressed when their impact and significance were uncertain. The study also found that implementing comprehensive BIM guidelines and client requirements influenced how design issues were identified and communicated to the project team. The research emphasizes the importance of AQAQC, design, and model coordination.