AUTHOR: Rosaria Manzo
TUTORS: Ing. Giovanni Franchi
INTERNSHIP: Impresa Pizzarotti & C. S.p.A.
MASTER: Master in “Project Management delle Opere Strutturali e Infrastrutturali” a.a 2021/22
ll seguente lavoro di tesi persegue l’obbiettivo di illustrare le conoscenze apprese durante il percorso di master in “Project Management delle Opere strutturali ed infrastrutturali” ed applicate nel corso dell’esperienza di stage presso “Impresa Pizzarotti & C. S.p.A.” in qualità di Cost Controller.
Il percorso di Stage è stato interamente svolto all’interno dell’Ufficio “Controllo di gestione” al fine di supportare le attività di Controllo di commessa in Italia e all’estero, con focus sul progetto “Infrastrutture stradali del Porto di Genova”.
La pianificazione, il controllo costi e la riprogrammazione sono attività che hanno una notevole rilevanza ai fini della riuscita della commessa; a tal proposito il controllo di gestione è quella funzione di analisi e controllo dei risultati economici aziendali basata sul confronto sistematico tra previsione e consuntivazione dei costi e dei ricavi, al fine di indagare l’andamento dei lavori.
Il seguente lavoro di tesi dimostra come la qualità di un progetto è fortemente correlata alle tre variabili che caratterizzano il “triangolo di gestione del progetto”: scope, tempo e costi. Tali variabili sono strettamente collegate tra loro e risulta indispensabile il loro equilibrio ai fini del soddisfacimento dei requisiti di progetto.
Dallo studio condotto emerge come gli strumenti di gestione siano fondamentali ai fini della buona riuscita di un progetto, in quanto in grado di garantire la qualità del progetto, e quindi la sua realizzazione nei tempi definiti, l’ottimizzazione delle risorse impiegate ed il controllo della produzione e dei costi rispetto a quanto preventivato.
In particolare, la definizione delle Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) risulta un primo supporto al miglioramento della pianificazione delle attività, a cui si connette e integra la schedulazione temporale di esecuzione delle fasi lavorative, attraverso il diagramma di Gantt, con conseguente facilitazione del controllo dei tempi e dei costi.
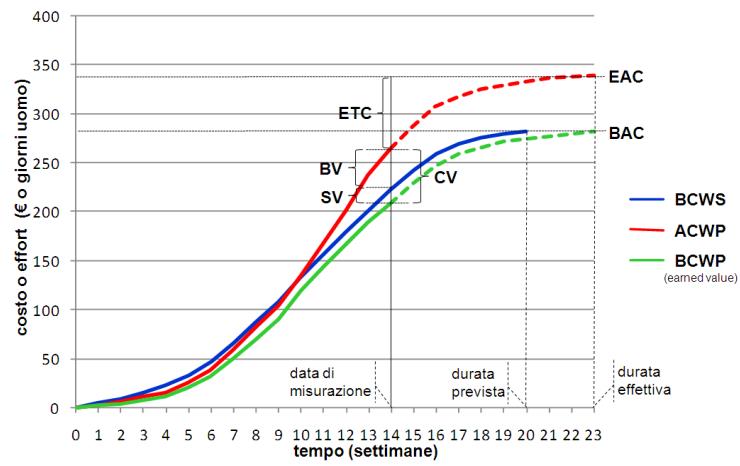
Il caso studio ripercorre l’applicazione del Metodo dell’Earned Value che, differentemente ai metodi tradizionali, consente di misurare le performance del progetto monitorando le tre dimensioni chiave che caratterizzano il progetto. Ciò consente di estrapolare un quadro dettagliato dell’andamento della commessa, permettendo di individuare eventuali problematiche/rischi in modo preventivo.
L’applicazione di tale metodo ad un caso studio fittizio, attraverso l’impiego del Software gestionale STR Vision e l’individuazione dei KPI principali, ha permesso l’individuazione ed il monitoraggio dello stato di avanzamento del progetto nonché l’identificazione delle principali efficienze ed inefficienze registratesi al time now.
Il risultato che ne consegue è una descrizione accurata dei principali scostamenti resa possibile attraverso un’analisi dei cruscotti estrapolati dal programma STR Vision, dai quali emerge come il progetto (caso studio fittizio) sia efficiente (costi actual minori dei costi previsti) ed efficace (anticipo sulla produzione) nonostante la presenza di varianti in corso d’opera non previste a Budget.
L’intero processo messo in atto mostra come l’applicazione del Metodo dell’Earned Value consenta una gestione efficace ed efficiente delle attività, sia in termini di tempo che di rispetto del budget, consentendo una valutazione globale ed approfondita della performance del progetto.
FOR INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS:
The following thesis work wants to illustrate the knowledge learned during the Master in “Project Management of structural and infrastructural works” and implemented during my internship in Impresa Pizzarotti & C. S.p.A in the role of Cost Controller.
This internship took place entirely in the Management Control office to support management control activities in Italy and abroad, with a special focus on the “Port of Genoa road and infrastructures” project.
Planning, cost controlling and re-programming have a crucial role for the success of the success of the project; in this regard, management control wants to analyse and control the company’s economic performance based on the systematic comparison between costs and revenues’ forecast and final balance, in order to investigate the progress of the works.
The aim of this thesis work is to show how the quality of a project is strongly related to the three variables characterizing the “project management triangle”: scope, time and costs. These three variables are closely linked to each other and their balance is essential to meet the project requirements.
The study conducted shows how the management tools are crucial for the success of the project, as they guarantee its quality and therefore its realization within the time limit, the optimization of the resources used and the production and costs’ control compared to the estimated ones.
Defining the WBS is the first support to improve the planning of activities linked and implemented by the execution of the work phases’ time schedule, through the diagram of Gantt, with consequent facilitation of time and costs control.
The case study follows the application of the Earned Value Method. Unlike the traditional methods, this one allows to measure the project performance monitoring the three key dimensions that characterize the project. This allows to extrapolate a detailed overview of the progress, allowing to preemptively identify any problems/risks.
Applying this method to a fictitious case study, helped by the STR Vision management software and the identification of the main KPIs, has made it possible to identify and monitor the progress of the project as well as the main efficiencies and inefficiencies recorded at “time now”.
The result is an accurate description of the main deviations made possible through an analysis of the dashboards obtained from the STR Vision program, from which it emerges that the project (fictitious case study) is efficient (actual costs are lower than budgeted costs) and effective (ahead of production) despite the presence of variances during construction that were not budgeted for.
This whole process shows how the application of the Earned Value method allows an effective and efficient management of the activities, both in terms of time and budget, enabling a global and in-depth assessment of the project’s performance.